Nodes Library
Bool, Int, Float, String, Color
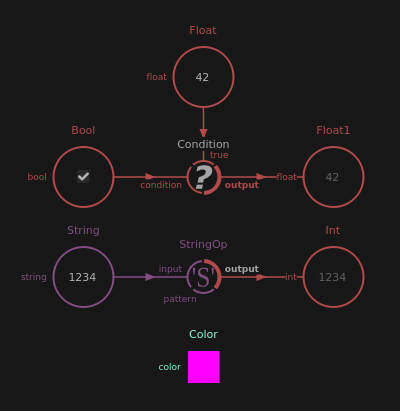
Those nodes provide a simple value with a widget to change or display it directly in the nodal graph.
V2i, V3i, V4i

Those nodes compose integer vectors.
V2f, V3f, V4f
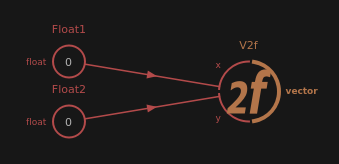
Those nodes compose floating point vectors.
Quatf
Quatf composes a quaternion.
M44f
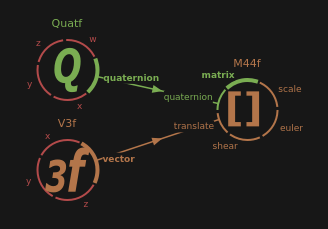
The M44f node composes a 4x4 matrix using the scale, shear, quaternion, euler angles and translation components.
The composition order, from left (first) to right (last) is : scale*shear*quaternion*euler*translate.
DecomposeM44f
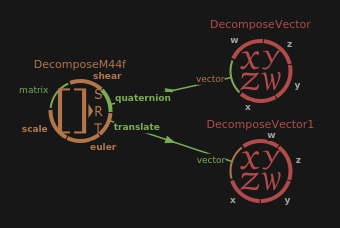
Decomposes a M44f value in scale, shear, euler anges, quaternion and translation.
The decomposition order is the same than used in the M44f node.
DecomposeVector
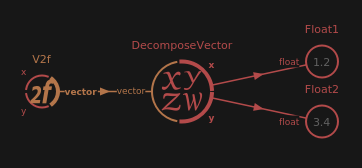
Decomposes a vector value like, V2f, V3f, V4f, V2i, V3i, V4i, Color or Quatf in X, Y, Z, W components.
Math
Rumba Rig provides a Math Node that can be configured to perform a set of mathematical operations:
Single Operators: taking input1 as argument
Logical (Bool and Int only): Not
Sign: Negative, Sign, Abs
Decimals: Ceil, Floor, Round, Trunc
Standard math functions: Inverse, Square, SquareRoot, Exp, Log, Log10, Cosinus, Sinus, Tangent, ArcCosinus, ArcSinus, ArcTangent
Vector operations: GetX, GetY, GetZ, GetW, Length, Length2, Normalize
Matrix operations: Transpose
Binary Operators: taking input1 and input2 as arguments
Comparison: Equal, NotEqual, Greater, GreaterOrEqual, Lesser, LesserOrEqual
Standard math operators: Addition, Subtraction, Multiply, Divide, Modulo, Minimum, Maximum, Power, ArcTangent2
Vector operations: Distance, DotProduct, CrossProduct
Vector-Matrix operations: TransformDirection, TransformPosition
Logic operators: And, Or, Xor
Bitwise operators: BitAnd, BitOr, BitXor, ShiftLeft, ShiftRightLogical, ShiftRightArithmetic
Math Nodes can be created directly from the operation name, e.g. Addition.
Some operations work on multiple types for which they have a definition, e.g. Inverse works for both Float and M44f Values.
The Math Node also works with Values like BufferFloat and BufferV3f.
AimConstraint
The AimConstraint Node takes a local transform and a parent transform as input and computes the modified local transform that points towards the weighted averaged position of a set of (world space) target transforms.
Inputs:
input: the initial local transform
parent_matrix: the parent transform
target_i: the i-th target transform
weight_i: the weight associated to the target_i
Note
The target weights are normalized internally.
Parameters:
aim_vector: The vector, in local space, that must point towards the target position.
up_vector: The local axis which must point upwards.
up_axis: The vector indicating the upward direction.
- up_mode: The interpretation mode of up_axis.
It can be a Local Axis or World Axis vector, a World Target position or Auto matically computed using closest rotation.
effect: How much input is modified to point towards the target position.
To set the number of target transforms, right-click the AimConstraint Node and select Resize. A popup window will open, enter the desired number of target transforms and press Resize or hit Enter.
Note
The AimConstraint Node has at least one target transform.
Constraint
The Constraint Node takes a local transform and a parent transform as input and computes the modified local transform so that its components match the weighted averaged components of a set of (world space) target transforms.
Inputs:
input: the initial local transform
parent_matrix: the parent transform
target_i: the i-th target transform
weight_i: the weight associated to the target_i
Note
The target weights are normalized internally.
Parameters:
constrain_scale: toggles the constraint on the scale component.
constrain_shear: toggles the constraint on the shear component.
constrain_rotation: toggles the constraint on the rotation component.
constrain_translation: toggles the constraint on the translation component.
effect: How much input is modified to match the target constraint components.
To set the number of target transforms, right-click the Constraint Node and select Resize. A popup window will open, enter the desired number of target transforms and press Resize or hit Enter.
Note
The Constraint Node has at least one target transform.